Range Test menu
This is a simple and quick test in which data packets are exchanged between two devices.
On the transmitter side, the device initiates the data transfer and expects to receive a packet containing the same data payload. An average RSSI calculation is performed based on the incoming packet’s RSSI and the number of sent packets. If the receiving packet does not contain the same data payload, RSSI calculation is not performed, and a ‘packet dropped’ message is shown in CLI.
On the receiver side, the device sends back the message to originator.
Range tests can be performed in three different modes:
Transmission without expected Acknowledgment.
Transmission with expected Acknowledgment.
Transmission with expected Enhanced Acknowledgment
Steps to perform a Range Test procedure
The steps to perform a Range Test procedure are as follows:
Set the source and destination address of the transmitter device:
source=0xaaaa,destination=0xbbb. (Any other addresses can be chosen). See the figure below.
Range Test: Set the source and destination addresses on TX side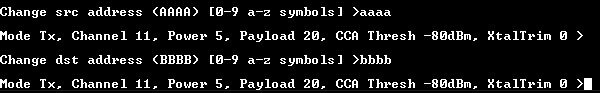
Set the source and destination address of the receiver device.
For example,
source=0xbbbb,destination=0xaaaa. (Any other addresses can be chosen). See the figure below.
Range Test: Set the source and destination addresses on RX side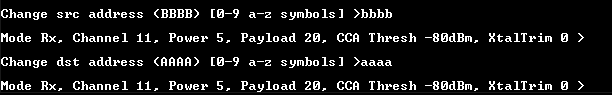
Set the receiver device to run as shown in the figure below.
Range Test: Set the RX device to run
Set the transmitter device to run.
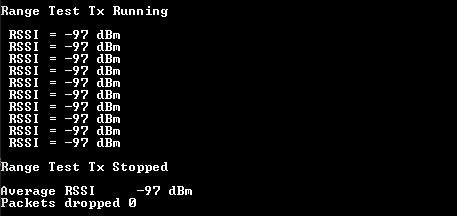
TX device CLI messages are shown in the figures below.
Range Test: TX device CLI messages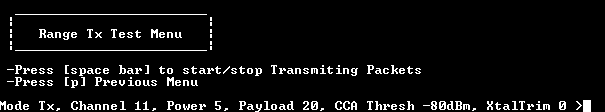 TX device CLI messages
TX device CLI messages
Receiver device CLI messages are as shown in the figure below.
Range Test: RX device CLI messages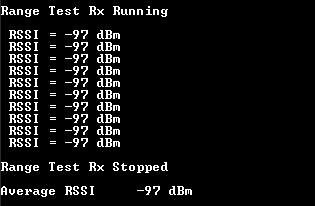
Parent topic:Range Test menu
Parent topic:CLI test description