i.MX RT bootable image
Bootable image layout in target flash device
There are two types of supported boot image:
XIP (Execute-In-Place) boot image: This type of boot image is only applicable to Serial NOR devices connected to QuadSPI or FlexSPI interfaces and Parallel NOR devices connected to WEIM or SEMC interface. The boot device memory is identical to the destination memory. ROM can boot this boot image directly.
Non-XIP boot image: This type of boot image is usually for the NAND, SD, and eMMC devices. The boot device memory is different from the destination memory. ROM loads the boot image from the boot device memory to the destination memory and then boots from the destination memory.
Bootable image layout
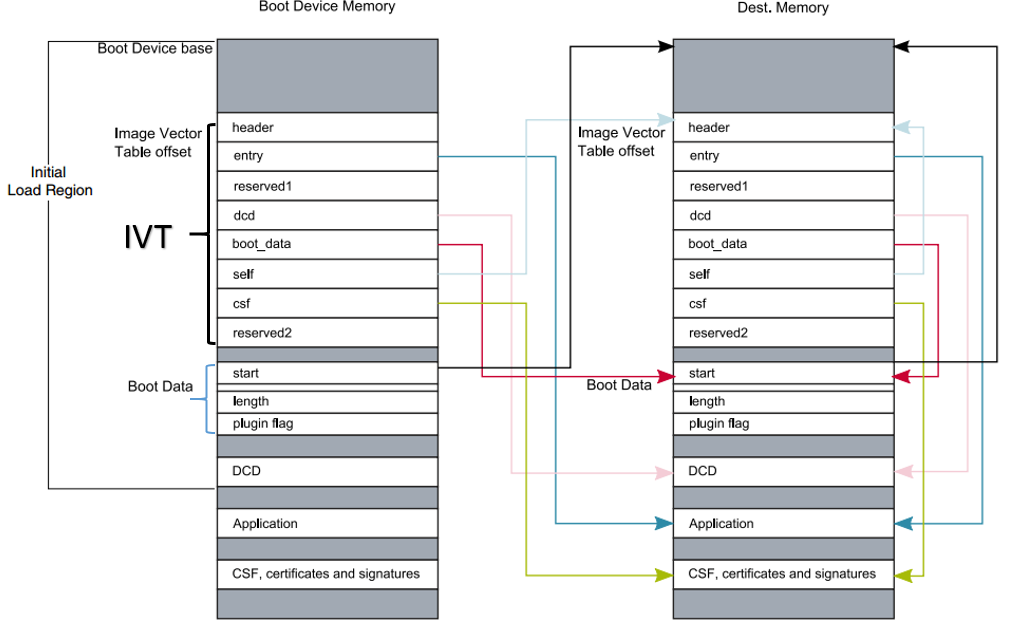
Parent topic:i.MX RT bootable image
Boot image format
This section describes the boot image format and data structures. The elftosb utility helps the customers automatically generate the boot image format file. The elftosb utility usage is described later in this document.
The bootable image must have the following data structures:
Image Vector Table (IVT): a list of pointers located at a fixed address that ROM examines to determine the location of other components of the bootable image
Boot Data: a table that indicates the bootable image location, image size in bytes, and the plugin flag
Device configuration data (DCD) (optional): IC configuration data configures DDR/SDRAM memory
User application and data
CSF (optional): signature block for Secure Boot generated by CST
KeyBlob (optional): a data structure consists of wrapped DEK for encrypt boot
Each bootable image starts with appropriate IVT. In general, for the external memory devices that support XIP feature, the IVT offset is 0x1000 else it is 0x400.
IVT and boot data
The IVT is the data structure that the BootROM reads from the boot devices. This data structure supplies the bootable image containing the required data components to perform a successful boot.
See the Program image section in the System Boot chapter of the device reference manual for more details.
IVT data structure
Offset |
Field |
Description |
|---|---|---|
0x00 - 0x03 |
header |
• Byte 0 tag, fixed to 0xD1 |
0x04 - 0x07 |
entry |
Absolute address of the first instruction to execute from the image, or the vector address of the image |
0x08 - 0x0b |
reserved1 |
Reserved for future use, set to 0 |
0x0c - 0x0f |
dcd |
Absolute address of the image DCD. It is optional, so this field can be set to NULL if no DCD is required |
0x10 - 0x13 |
boot_data |
Absolute address of the boot data |
0x14 - 0x17 |
self |
Absolute address of the IVT |
0x18 - 0x1b |
csf |
Absolute address of the Command Sequence File (CSF) used by the HAB library |
0x1c - 0x1f |
reserved2 |
Reserved, set to 0 |
Parent topic:Boot image format
Boot data structure
Boot Data structure
Offset |
Field |
Description |
|---|---|---|
0x00-0x03 |
start |
Absolute address of the bootable image |
0x04-0x07 |
length |
Size of the bootable image |
0x08-0x0b |
plugin |
Plugin flag, set to 0 because plugin boot is not supported on the RT1010 |
Parent topic:Boot image format
Parent topic:i.MX RT bootable image
Signed image
The bootable image can be signed by CST tool. The tool generates the CSF data in the binary file format that consists of command sequences and signatures based on given input command sequence file (csf file). Refer to the documentation in the CST release package for further details.
In this document, a simple method is introduced to generate signed images using the elftosb utility.
Parent topic:i.MX RT bootable image
Encrypted image
There are two types of encrypted image formats:
Encrypted XIP image format
The Flashloader generates the encrypted XIP image using the AES CTR algorithm when programming the image on the device. On execution, the hardware engine does on-the-fly decryption.
Encrypted image generated by CST
To increase the security level, the bootable image can be signed and further encrypted by the CST. The KeyBlob must be generated on the device. The hardware deletes all sensitive keys if any security violation happens so that the sensitive keys cannot be cloned.
In this document, a simple method is introduced to generate signed images using the elftosb utility.
Parent topic:i.MX RT bootable image