Configuration System Based on Kconfig
Overview
Kconfig is a selection-based configuration system originally developed for the Linux kernel which now found more and more use in other projects beyond the Linux kernel.
In MCUXpresso SDK, Kconfig is used to config the build in runtime which includes component selection with dependency resolve, component configuration with feature enable, disable and customization.
You can interact with Kconfig via a curses or graphical menu interface, usually invoked by running west build -t guiconfig after you have already run passed the CMake configuration process. In this interface, the user selects the options and features desired, and saves a configuration file which is then used as an input to the build process.
Kconfig Usage
Please install python3 before installing kconfiglib. For kconfiglib, you can run with the command
pip install -U kconfiglib
Make sure that MCUXpresso SDK core, devices, boards repositories have been cloned.
Run
Inside Kconfig files, there are board/device variables included in referenced paths, so it cannot be directly run. The Kconfig shall be run during the example cmake build process.
Run cmake configuration
west build -b evkbmimxrt1170 examples/demo_apps/hello_world -Dcore_id=cm7 --cmake-only -p
--cmake-onlyonly executes build system configuration stage and generation stage. If you omit--cmake-only, then the project will be built.Run guiconfig target
west build -t guiconfig
Then you will get the Kconfig GUI launched, like
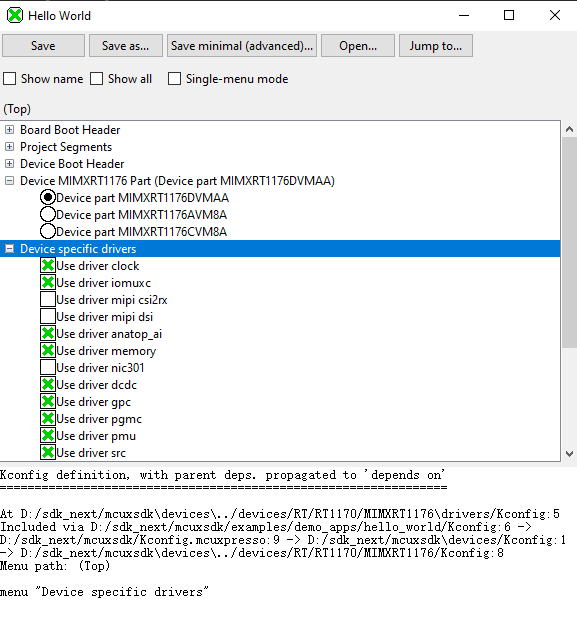
You can select/deselect and modify to do reconfiguration.
After you save and close, you can directly run
west buildto do the build.
Kconfig Process Flow
The input are Kconfig files and prj.conf with priority. The direct output is the .config and config headers. Any updates in input Kconfig, output .config and config header will trigger a Kconfig process in next build cmd.
prj.conf
prj.conf is the pre set value for Kconfig symbols. It is the input for the Kconfig process. Unlike the cmake files which shall be explicitly included, the proj.conf will be loaded implicitly.
The prj.conf search paths can be provided through 3 ways with priority.
Default prj.conf search paths
For all project build, the following prj.conf paths will anyway be collected into the build. They are related to device, board and example board specific part. The priority is from low to high. High priority prj.conf data will override low priority prj.conf data.
1. devices/prj.conf 2. devices/<soc_series>/prj.conf 3. devices/<soc_series>/<device>/prj.conf 4. devices/<soc_series>/<device>/<core_id>/prj.conf 5. examples/prj.conf 6. examples/_boards/prj.conf 7. examples/_boards/<board>/prj.conf 8. examples/_boards/<board>/<core_id>/prj.conf 9. examples/<example_category>/prj.conf 10. examples/<example_category>/<example>/prj.conf 11. examples/_boards/<board>/<example_category>/prj.conf 12. examples/_boards/<board>/<example_category>/<example>/prj.conf 13. examples/_boards/<board>/<example_category>/<example>/<core_id>/prj.conf
For shield case, it is generally the same as board:
1. devices/prj.conf 2. devices/<soc_series>/prj.conf 3. devices/<soc_series>/<device>/prj.conf 4. devices/<soc_series>/<device>/<core_id>/prj.conf 5. examples/prj.conf 6. examples/_boards/prj.conf 7. examples/_boards/<board>/prj.conf 8. examples/_boards/<board>/<core_id>/prj.conf 9. examples/<shield_example_category>/prj.conf 10. examples/<shield_example_category>/<example>/prj.conf 11. examples/_boards/<board>/<shield>/prj.conf 12. examples/_boards/<board>/<shield>/<shield_example_category>/prj.conf 13. examples/_boards/<board>/<shield>/<shield_example_category>/<example>/prj.conf 14. examples/_boards/<board>/<shield>/<shield_example_category>/<example>/<core_id>/prj.conf
If the
projectmacro is withNO_DEFAULT_CONFIGlike the following, then build system will skip all the default prj.conf search paths. Since the input prj.conf cannot be empty, so the prj.conf must be provided withCUSTOM_PRJ_CONF_PATHorDCONF_FILE.project(hello_world LANGUAGES C CXX ASM NO_DEFAULT_CONFIG)
Specify customized prj.conf search path(s) in project CMakeLists.txt
projectwithCUSTOM_PRJ_CONF_PATHThe
CUSTOM_PRJ_CONF_PATHargument can be used in project CMakeLists.txtprojectmacro to specify the customized prj.conf search paths and they have higher priority than the default prj.conf search paths.It could be either relative path or absolute path. For relative path, the root is the MCUXpresso SDK root.
Here is one example:
project(hello_world LANGUAGES C CXX ASM PROJECT_BOARD_PORT_PATH examples/_boards/${board}/demo_apps/hello_world CUSTOM_PRJ_CONF_PATH subfolder e:/mcuxsdk/subfolder)
The
mcuxsdk-root/subfolder/prj.confande:/mcuxsdk/subfolder/prj.confwill be added into build if existed.-DCONF_FILE=<customized config file>
You can directly provide customized prj.conf with
-DCONF_FILE=<customized config file>, likewest build -b evkbmimxrt1170 examples/demo_apps/hello_world -Dcore_id=cm4 -DCONF_FILE=./examples/prj.conf
The customized project config file has the highest priority over all.
.config
.config will be read back by cmake after generated. It has all the resolved device, board, drivers, components, middlewares Kconfig symbols and values. Its contents will be filtered to get the dependency satisfied components and project segments symbols, such symbols will be put into later cmake process so that cmake knows which components and project segments data shall be included into the build process.
All the components and project segments Kconfig symbols start with
CONFIG_MCUX_COMPONENT_orCONFIG_MCUX_PRJSEG_. They won’t be generated into config header files.
For example, if CONFIG_MCUX_COMPONENT_driver.uart is y in .config, then the following sources and includes will be added into the build during cmake process, otherwise not.
if(CONFIG_MCUX_COMPONENT_driver.uart)
mcux_add_source(
SOURCES fsl_uart.h
fsl_uart.c
)
mcux_add_include(
INCLUDES .
)
endif()
Config Headers
The Kconfig symbols and the values related to compile and link will be generated into config header files placed in build binary folder.
Except Kconfig symbols starting with
CONFIG_MCUX_, all other Kconfig symbols with their values will be generated into config header files.
If you want your components configuration Kconfig symbols and values to be generated into designated header file, you can set Kconfig menu with header name. Here is an example with Freertos kernel.
menu "Configuration (FreeRTOSConfig_Gen.h)" # All freertos kernel Kconfig symbols and values will be generated into FreeRTOSConfig_Gen.h
#******************************************************************************#
#* Hardware description related definitions. **********************************#
#******************************************************************************#
config configCPU_CLOCK_HZ
string "configCPU_CLOCK_HZ"
default "(SystemCoreClock)"
help
No prefix in generated macro
In this way, all the Kconfig symbols inside menu "Configuration (FreeRTOSConfig_Gen.h)" will be generated into FreeRTOSConfig_Gen.h.
For such customized header files, there are 2 ways to include them into build tree:
The build binary folder is added into search path by default, you just need to include the config headers in the source in advance so that all config header files will be added into build tree. This is the default way.
If you run with
-DPREINCLUDE=1, then all generated header files will be included into build tree in a preinclude way.
If it is not set, then all Kconfig symbols and values will be generated header named mcux_config.h which will be added into project in a preinclude way.
MCUXpresso SDK Customized Kconfig Rules
To support MCUXpresso SDK development, we introduce some customized Kconfig rules. These rules could be used together.
Introduce Component, Project Segment and Dependency Definition Symbols
To support Componentization and Complex Dependency, we introduce some customized Kconfig symbol definitions with the following namings:
Naming |
Functionality |
|---|---|
|
Specify the Kconfig symbol is a component. |
|
Specify the Kconfig symbol is a project segment. |
|
Specify the dependency for component. |
|
Specify the dependency of component 1 on component 2, mainly used to display the dependency in |
|
Specify the hardware information, mainly for dependency purpose. The device Kconfig.chip is the major definition file for such Kconfig symbol. |
The above naming Kconfig symbols are used to define components, project segments and the dependencies.
All Kconfig symbols with above naming prefix MCUX_ will be intentionally removed out of the generated config header file. All other Kconfig symbols will be regarded as compile and link used macros and generated into header file to be involved in the build process.
Remove CONFIG_ Prefix for Macro Name
Kconfig by default will add CONFIG_ prefix to macros in the generated header files. However, this prefix doesn’t work for some middlewares or RTOSes, like fafts and freertos. Their sources complication cannot work with macros with prefix CONFIG_ . To support such cases, we introduced a mechanism to forbid adding CONFIG_ prefix in the macros: in the help of the Kconfig symbol, No prefix in generated macro shall be provided, like
config RAM_DISK_ENABLE
bool "RAM"
default y if MCUX_COMPONENT_middleware.fatfs.ram
default n
help
No prefix in generated macro
Then the generated macro in header file is like
#define RAM_DISK_ENABLE 1
Keep Quotes for String Type Macro Value
If the Kconfig symbol value is string type, for C language it must be wrapped with quotes. This requires value set in Kconfig’s default or prj.conf must be escaped from quotes using \" which is not convenient, like:
config CHIP_DEVICE_PRODUCT_NAME
string "Product name"
default "\"not-specified\""
help
Provides a human-readable product name
To get rid of the escape characters, we introduce the mechanism: for string type Kconfig, if Macro value is in quotes is provided in help, then quotes will be kept in the generated macro. The above CHIP_DEVICE_PRODUCT_NAME can be wrote this way:
config CHIP_DEVICE_PRODUCT_NAME
string "Product name"
default "not-specified"
help
Provides a human-readable product name
Macro value is in quotes
Then the generated macro in header file is like
#define CONFIG_CHIP_DEVICE_PRODUCT_NAME "not-specified"
Keep U Suffix for Unsigned Integer Type Macro Value
Unlike C, Kconfig only provides integer data types. If you want to mark data as unsigned integer, please add type unsigned keyword in Kconfig help information.
Here is an example, the following Kconfig symbol
config USB_DEVICE_CONFIG_HID
int "HID (Human Interface Device) Instance Count"
default 0
help
No prefix in generated macro
type unsigned
will be generated into macro like:
#define USB_DEVICE_CONFIG_HID 0U