MCUBoot and NXP encrypted XIP extension
1. Introduction
To provide confidentiality of image data while in transport to the device or while residing on an non-secure storage such as external flash memory, MCUboot has support for encrypting/decrypting images on-the-fly while upgrading. The design expects that XIP is done from an secure memory so authenticated encrypted image is decrypted to a secure location such as internal Flash or RAM.
Some NXP devices support encrypted XIP on an internal or external Flash device utilizing on-the-fly decryption modules (BEE, OTFAD, IPED, NPX…). Is possible use these dencryption engines with a second stage bootloader as the MCUBoot.
This document describes an extension of MCUBoot functionality to support encrypted XIP on NXP devices and its enablement in OTA examples in MCUXpresso SDK.
2. MCUBoot encrypted image
In the extension the encrypted image by MCUBoot is used as secure capsule for transport and staging in non-xip area of device.
In summary, an image payload is encrypted using AES-CTR cipher by image tool (see imgtool). The AES key is randomized per OTA image and padded to image as an encrypted TLV section. The encrypted AES key can be decrypted using private key in selected key encryption scheme (RSA-OAEP, AES-KW, ECIES-P256 or ECIES-X25519).
Following image shows keys management of MCUboot encrypted image.
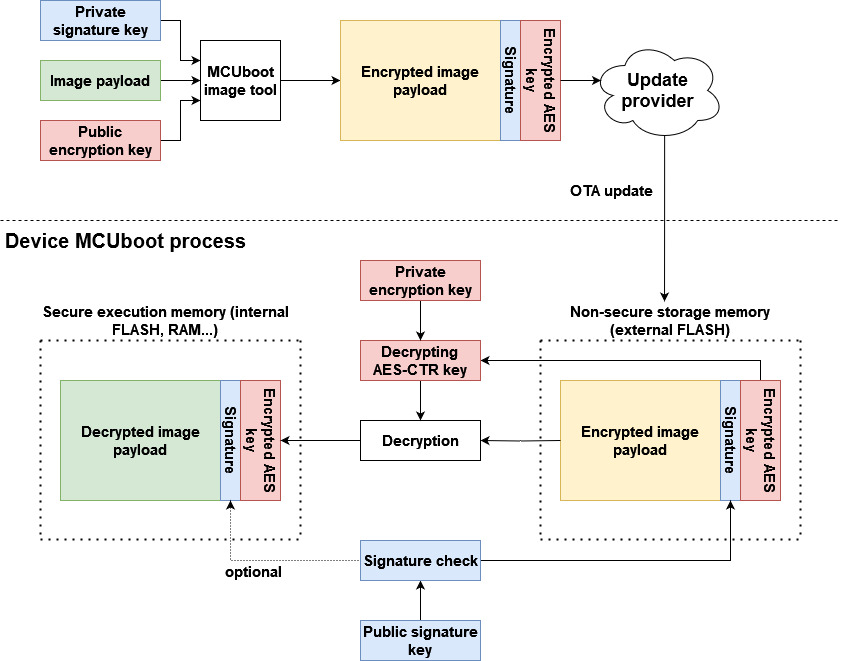
Note: Current version of MCUboot (2.0.0) doesn’t support hardware format of private key using trusted sources (OTP, TPM…) and currently supports only private key embed as an array in MCUboot code (see middleware\mcuboot_opensource\boot\nxp_mcux_sdk\keys.c). User is advised to implement secure provisioning and loading of the private key in device, for example by encrypting the MCUboot or staging private key in encrypted secure area. Support of hardware keys for encrypted images is targeted for next release of MCUboot. For simplicity the ota examples in SDK uses unencrypted MCUBoot application so there is no need for provisioning of device.
For more information please see MCUBoot Encrypted images documentation.
3. Encrypted XIP extension for MCUboot
The extension combines usage of platform specific encryption module and funcionality of MCUBoot encrypted images created by imgtool.
Following image shows simplified OTA update flow of device fleet using encrypted XIP extension.
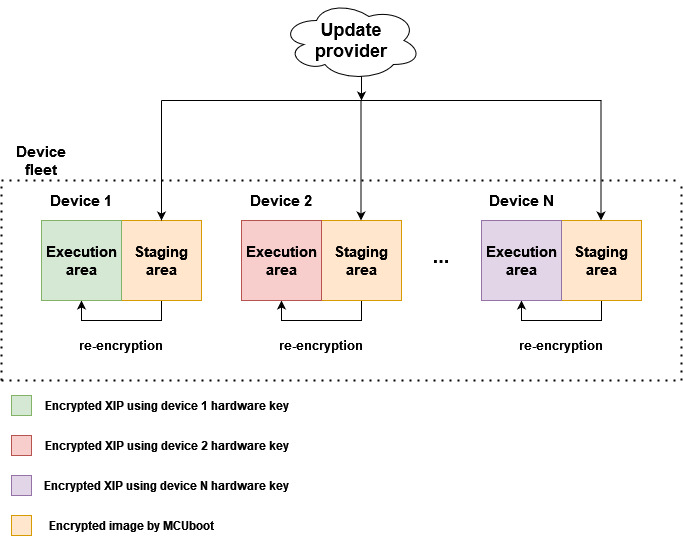
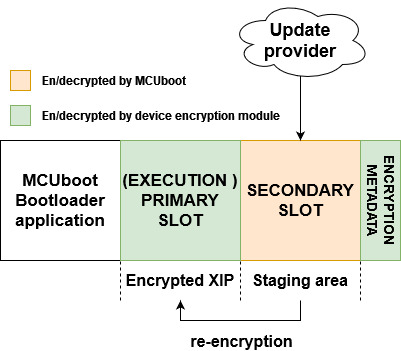
Device fleet shares MCUBoot private key used for decryption of encrypted OTA images residing on staging areas. The MCUBoot AES key and hardware encryption module are then used for image re-encryption to the execution area. Hardware key is provisioned by NXP or user and is typically unique per device instance to prevent image cloning.
3.1 Configuration structures
In summary, every NXP encryption unit utilizing encrypted XIP uses a scheme where on-the-fly decryption is configured by ROM. After device reset, the ROM investigates specific configuration structures expected typically at particular flash offset of header of bootable image. If configuration structures consisting encrypted keys and IVs are valid then the ROM configures the encryption unit.
In case of OTA update it is expected that for security reasons we have to update key and/or IV of encrypted execution region so also these configuration blocks have to be re-generated. Unfornately this creates a risk during updating these configuration blocks as there is a period in time where a power-loss could corrupt the update and result in bricked device.
Note: The issue is related to only second stage bootloader usage. OTA solutions using only ROM bootloader typically utilize dual image feature which safely handles this issue.
The risk is resolved by moving configuration blocks out of the header of the second stage bootloader at a particular flash area and let SBL configure encryption module manually by inspecting these configuration blocks.
The encrypted XIP extension uses reserved area called encryption metadata what is used for storage of configuration blocks and encrypted XIP handling. Following image shows general structure of encryption metadata.
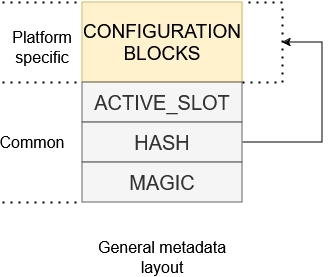
The metadata sector consists platform specific configuration blocks and common confirmation block. The slot number is pointer to slot containing selected image extracted from MCUBoot response object. The hash acts as confirmation of integrity of configuration blocks and content in execution slot.
During an OTA update the extension generate new configuration block with IV, write it at particular flash offset and reconfigure encryption unit for execution area. If the update and verification of the execution area are successful the configuration block is then hashed and confirmed by writing confirmation block.
3.2 Modes of the extension
The extension utilize layout with one execution slot for encrypted XIP and one or two slots for staging OTA image. Partition layout can be configured in two configuration modes which are summarized in following table
Extension mode |
required flash size |
revert (self-test) support |
MCUBOOT update mode |
|---|---|---|---|
Three slot |
SBL + 3 x slot size + metadata sector |
yes |
DIRECT-XIP |
Overwrite-only |
SBL + 2 x slot size + metadata sector |
no |
MCUBOOT_OVERWRITE_ONLY |
3.2.1 Three slot configuration
Following image shows flash memory layout using MCUboot bootloader in DIRECT-XIP mode and encrypted XIP extension using three slot configuration.
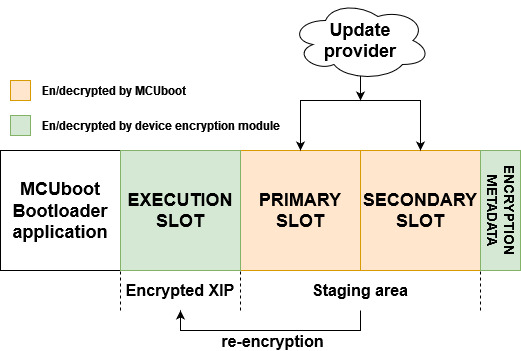
Primary and secondary slot act as a staging area for encrypted OTA images and the execution slot is used as an execution area of encrypted image using platform on-the-fly decryption. The encrypted XIP is emulated by execution of working copy of authentized image by MCUboot.
Initial process of authentication and selection (active flag) of an image by MCUBoot is then extended by re-encryption of the selected image to the execution slot. This operation is handled by a post-bootloader process what is out of context of MCUboot and it is basically plugged just before jumping the selected image by MCUboot. The re-encryption is only done for new image selection, otherwise the content of execution slot is just validated for integrity against selected image in staging area. The process is demonstrated in module encrypted_xip_mcuboot_support.c.
Following image shows direct-xip flow of MCUBoot extended with encrypted XIP support.
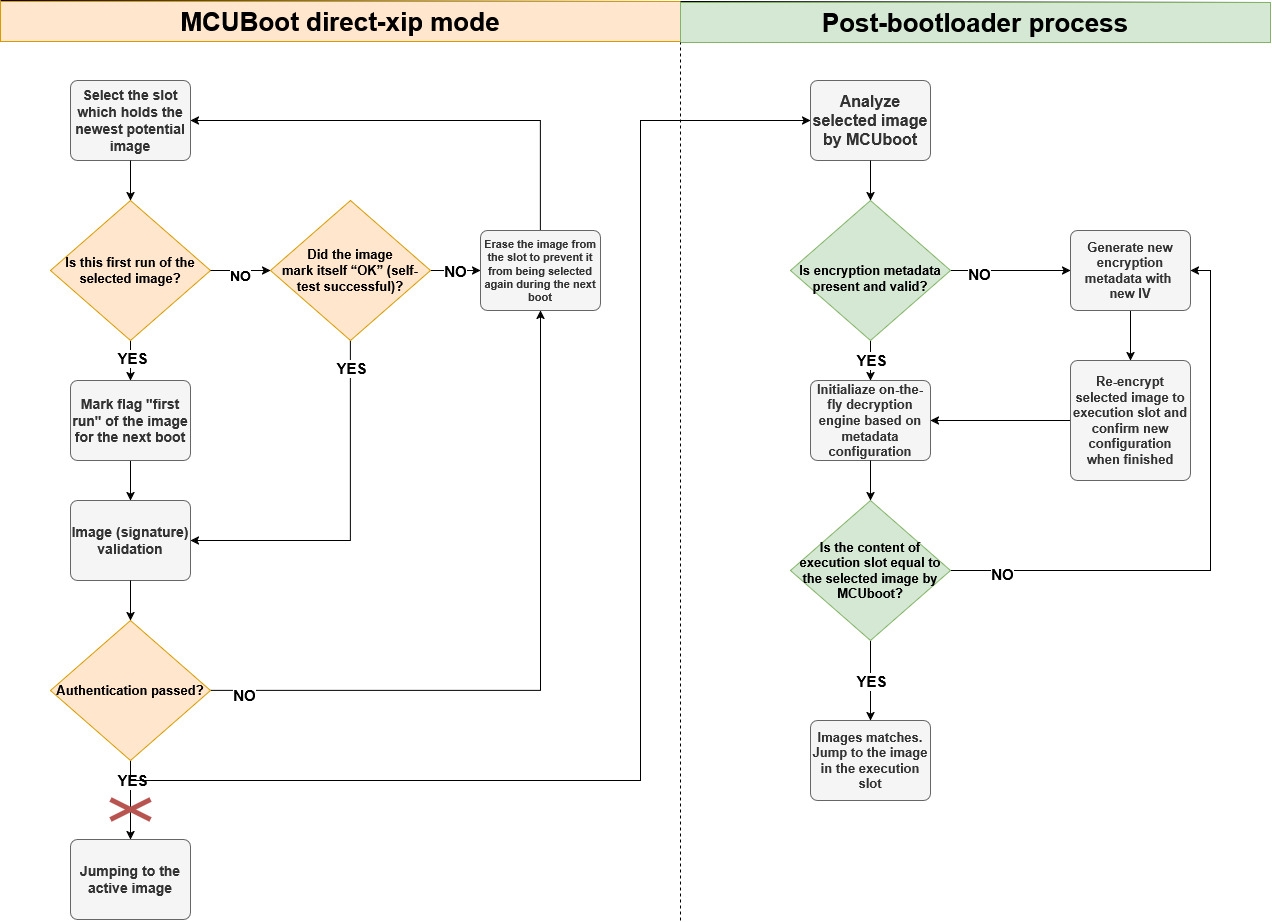
Note: the placement of metadata in this mode is up to user. The metadata block can be stored at the end of the execution slot as the original mcuboot trailer is not used there anyway.
3.2.2 Overwrite-only mode
This mode is much simpler but lacks revert functionality as there is only one staging slot.
Following image shows simplified flow of MCUBoot overwrite-only mode extended with encrypted XIP extension.
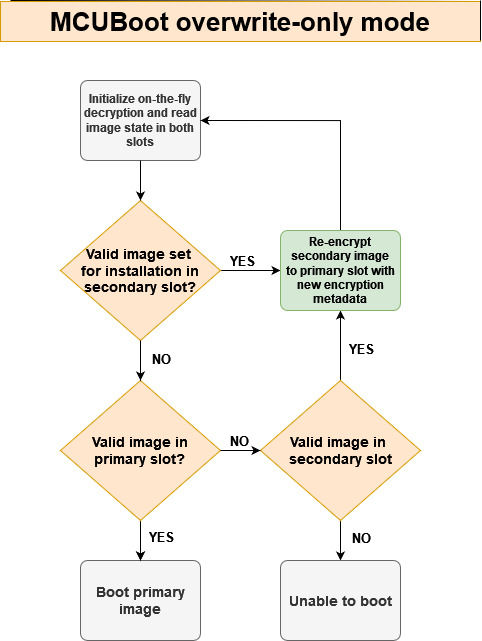
Before jumping to booting process the on-the-fly decryption is initialiazed so MCUboot is able to read and validate content in primary slot. Re-encryption process is implemented in customized MCUboot code and in MCUBoot hooks (see flash_api.c and bootutil_hooks.c).
4. NXP encryption engines
4.1 BEE (Bus Encryption Engine)
This peripheral is specific for RT10xx (except RT1010) and supports up two separate regions using two separate AES keys. In this solution, BEE region 1 is used for encrypting execution slot and BEE region 0 is reserved for a bootloader.
BEE configuration blocks are organized as EPRDB (Encrypted Protection Region Descriptor Block), where the EPRDB is encrypted using AES-CBC mode with AES key and IV located in KIB (Key Info Block). The KIB is encrypted as EKIB (Encrypted KIB) using key provisioned by user. Each BEE region has its PRDB/KIB pair.
The EKIB is decrypted by a key based on selection in BEE_KEYn_SEL fuse:
Software key
default value in
BEE_KEYn_SELevaluating BEE without fusing the device
SW-GP2
fused by user and typically used for offline encryption
limited funcionality due hardware bugs, see errata
not supported in this solution
OTPMK
provisioned by NXP in factory
unique per device instance - prevents image cloning
recommended
Following image shows complete metadata structure used for devices with BEE.
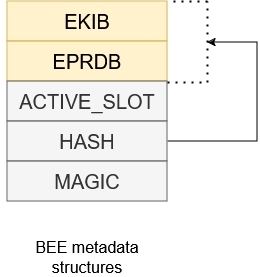
Firmware in execution slot is de/encrypted using AES-CTR combining nonce extracted from PRDB and this device key. The extension automatically detects device key by evaluating BEE_KEYn_SEL fuse.
The whole BEE initialization and encryption metadata handling is resolved in module encrypted_xip_platform_bee.c.
Additional information can be found in Security Reference Manual of target device and in AN12800, AN12852 and AN12901.
4.2 OTFAD (On-the-Fly AES Decryption Module)
To be implemented…
4.3 IPED (Inline Prince Encryption/Decryption for off-chip flash)
IPED is encryption unit for external flash specific for NXP RW61x, RT700 and MCXN MCUs.
Note: The extension currently supports only IPED module in RW61x based on GCM algorithm.
Following image shows configuration of metadata structure used for devices with IPED.
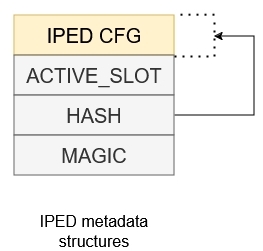
There are several points when using IPED especially in GCM mode
Consumption of physical memory when GCM algorithm is used
range of IPED region is defined in terms of logical address but the physical memory consumption is 1.25 times the logical memory consumption
OTA process must ensure that installed OTA image doesn’t overlap size of IPED region, for example by adjusting the text size in linker file and doing checks of re-encrypted image size
Flash operations have to satisfy boundaries of the flash page/sector size and encryption unit size
see “Constraints on IPED regions” chapter in reference manual
The whole IPED initialization and encryption metadata handling is resolved in module encrypted_xip_platform_iped.c.
Additional information for IPED in RW61x can be found in its reference manual.
4.4 NPX (PRINCE encryption/decryption for on-chip flash)
To be implemented…
5. OTA examples instructions
Start preferentially with an empty board, erasing original content if needed.
5.1 Generate RSA key pairs for encrypted image containers
Note: This part can be skipped as OTA examples in SDK uses pre-generated key pairs.
Generate private key
imgtool keygen -k enc-rsa2048-priv.pem -t rsa-2048
Adjust the content of the middleware\mcuboot_opensource\boot\nxp_mcux_sdk\keys\enc-rsa2048-priv.pem accordingly.
Extract private key to C-array
imgtool getpriv --minimal -k enc-rsa2048-priv.pem
Adjust the content of the middleware\mcuboot_opensource\boot\nxp_mcux_sdk\keys\enc-rsa2048-priv-minimal.c accordingly.
Derive public key key
imgtool getpub -k enc-rsa2048-pub.pem -e pem
Adjust the content of the middleware\mcuboot_opensource\boot\nxp_mcux_sdk\keys\enc-rsa2048-pub.pem accordingly.
5.2 Enable encrypted XIP support and build projects
Encrypted XIP can be evaluated by enabling define CONFIG_ENCRYPT_XIP_EXT_ENABLE in sblconfig.h.
Optional overwrite-only mode is enabled by CONFIG_ENCRYPT_XIP_EXT_OVERWRITE_ONLY.
Note: make sure that define CONFIG_MCUBOOT_FLASH_REMAP_ENABLE is disabled otherwise builds fails.
Build mcuboot_opensource and OTA application.
Load mcuboot_opensource.
5.3 Sign and encrypt image
To sign and encrypt an application binary, imgtool must be provided with respective key pairs and a set of parameters as in the following examples:
The initial image must be loaded using the –pad –confirm parameters regardless if using ISP or other method to write it For an initial image use following set of commands:
imgtool sign --key sign-rsa2048-priv.pem
--align 4
--header-size 0x400
--pad-header
--slot-size 0x200000
--max-sectors 800
--version "1.0"
--pad
--confirm
-E enc-rsa2048-pub.pem
app_binary.bin
app_binary_SIGNED_ENCRYPTED_INITIAL.bin
For an OTA image just remove the parameters --pad --confirm and increase the version number as in the following set of commands:
imgtool sign --key sign-rsa2048-priv.pem
--align 4
--header-size 0x400
--pad-header
--slot-size 0x200000
--max-sectors 800
--version "1.1"
-E enc-rsa2048-pub.pem
app_binary.bin
app_binary_SIGNED_ENCRYPTED_OTA.bin
The values of parameters can be obtained from a readme file of target board. Example: boards\BOARD\ota_examples\mcuboot_opensource\example_board_readme.md
Note: The parameters --pad --confirm for an initial image applies only for three slot mode as direct-xip setup is used and it requires presence of the slot trailer. Note that the size of generated binary equals size of the slot. For overwrite only mode an OTA image can be used as an initial image as the slot trailer is not required.
5.4 Evaluate encrypted XIP example
There are two methods how to run device for first time when application uses encrypted XIP.
5.4.1 Load encrypted image container to flash memory
Look into flash_partitioning.h for your target.
For three slot configuration you will find:
/* Encrypted XIP extension: Three slot mode */
#define BOOT_FLASH_EXEC_APP 0x60040000 -- execution slot address
#define BOOT_FLASH_ACT_APP 0x60240000 -- primary staging slot address
#define BOOT_FLASH_CAND_APP 0x60440000 -- secondary staging slot address
#define BOOT_FLASH_ENC_META 0x60640000 -- encryption metadata address
Image generated with additional --pad --confirm can be loaded to primary or secondary slot.
For overwrite-only configuration you will find:
/* Encrypted XIP extension: modified overwrite-only mode */
#define BOOT_FLASH_ACT_APP 0x60040000 -- active (execution) slot address
#define BOOT_FLASH_CAND_APP 0x60240000 -- candidate slot address
#define BOOT_FLASH_ENC_META 0x60440000 -- encryption metada address
#define BOOT_FLASH_EXEC_APP BOOT_FLASH_ACT_APP
Image has to be loaded always to candidate slot address. Additional --pad --confirm parameters are not needed here.
To load image the pyocd, blhost or MCUXpresso Secure Provisioning Tool can be used.
Note: Is possible to attach to running encrypted application for debug purpose.
5.4.2 Run unsigned unencrypted OTA application (debug session)
An unsigned unencrypted application can be loaded and run using a debug session. When performing an OTA update the application responses with warning:
WARNING: invalid metadata of execution slot - debug session?
WARNING: OTA image will be downloaded to secondary slot
This is expected as there is no encryption metadata due debug purpose so application has no reference to linkage to referenced image in staging area.
5.5 Running encrypted image
These are expected outputs when an OTA image is detected and then re-encrypted
Three slot configuration:
hello sbl.
Bootloader Version 2.1.0
Primary slot: version=1.0.0+0
Image 0 Secondary slot: Image not found
writing copy_done; fa_id=0 off=0x1fffe0 (0x43ffe0)
Image 0 loaded from the primary slot
Starting post-bootloader process of encrypted image...
Referenced image is located in the primary slot
Decrypting and loading the MCUBOOT AES-CTR key for staged image...
AES-CTR key loaded
Checking the execution slot...
No valid image found in staging area...
Preparing execution slot for new image
BEE configuration found and successfully configured...
Installing new image into execution slot from staged area...
Erasing the execution slot...
erased 12/12 sectors
Re-encrypting staged image to execution slot...
processed 38724/38724 bytes
Loading image successful
Image verification successful
Post-bootloader process of encrypted image successful
Bootloader chainload address offset: 0x40000
Reset_Handler address offset: 0x40400
Jumping to the image
*************************************
* Basic MCUBoot application example *
*************************************
Built Feb 13 2025 16:06:06
$
Overwrite-only mode:
hello sbl.
Bootloader Version 2.1.0
On-the-fly decryption initialization completed
Image index: 0, Swap type: test
Image 0 upgrade secondary slot -> primary slot
Erasing the primary slot
On-the-fly decryption initialization completed
Image 0 copying the secondary slot to the primary slot: 0x9734 bytes
writing magic; fa_id=0 off=0x1ffff0 (0x23fff0)
erasing secondary header
erasing secondary trailer
Bootloader chainload address offset: 0x40000
Reset_Handler address offset: 0x40400
Jumping to the image
*************************************
* Basic MCUBoot application example *
*************************************
Built Feb 13 2025 16:06:06
$